Fc-mediated effector functions may play a key role in the mechanism of action of therapeutic antibodies while unwanted Fc receptor binding of biotherapeutics may severely affect clinical safety.
The EMA and FDA guidelines recommend analysing the Fc-mediated effector functions and cytotoxicity like Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC), Antibody Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP), Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC), binding to Fc gamma receptors and complement component C1q.
IBR Inc. offers full GxP compliant assessment of Fc-mediated effector functions, including cell-based assays and advanced technologies (Meso Scale, Alpha Technology, TR-FRET, Gyrolab, etc.). In addition, ADCC, ADCP, and CDC as well as binding of therapeutic molecules to the Fc gamma receptors and complement component C1q are important methods of the functional testing of biologicals. |
|
| |
|
| |
| | | | | | Binding to Fc gamma and neonatal Fc receptors
AlphaLISA competitive binding assays |
| | | Fcγ RIIIa (CD16a) is considered to be the main contributor to ADCC. It is expressed on NK cells, monocytes/macrophages, T-cells, granulocytes and eosinophils. Due to genetic polymorphism Fcγ RIIIa, a conventional type I transmembrane protein, is expressed in two isoforms, a high binding and a low binding variant. Fcγ RIIIb (CD16b) is a GPI anchored protein, which lacks a transmembrane domain and is expressed on neutrophils. Despite its function is not yet fully understood, there are evidences that Fcγ RIIIb (CD16b) synergizes with Fcγ RIIa (CD32a), which is predominantly expressed on cells of the myeloid lineage and has been demonstrated to contribute to ADCC and ADCP. Fcγ RIIb/c is expressed on NK cells, monocytes/macrophages, B cells, neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. It acts as an inhibitor of cell activation and ADCP. Fcγ RI (CD64) is the only high affinity Fc Receptor. It is expressed on dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, activated granulocytes and is involved in MHC dependent antigen presentation and cell activation.
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) is broadly expressed in different tissues. It prevents proteolytic degradation of IgGs thereby prolonging their half-life in circulation.
For non cell-based detection of human IgG binding to Fcγ receptors several ready-to-use AlphaLISA kits are available which cover the whole Fc receptor panel (FcγRIIIa - CD16a high and low binding variants; FcγRIIIb - CD16b; FcγRIIa - CD32a high and low binding variants; FcγRIIb - CD32b; FcγRI - CD64) and in addition FcRn.
Example data of AlphaLISA binding of different IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4) to Fc gamma and neonatal Fc receptors: |
|
| |
|
| | | | | 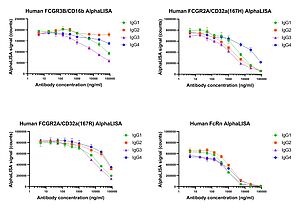 |
|
| | | | | | | | | Fc binding to Fc gamma receptors on cells can be assessed using any commercially available cell line or gene reporter cell line expressing Fcγ receptors by flow cytometry, gene reporter assays or employing the Cisbio cellular binding platform, based on Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF). |
|
| |
|
| |
| | | | | | Binding to C1q
Our in-house developed C1q ELISA |
| | | Binding of antibody – antigen complexes to the complement component C1q triggers the classical pathway of complement activation and results in the formation of the membrane attack complex leading to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Antibodies of the IgG subclasses IgG1, IgG2 and IgG3 (except IgG4) as well as IgM antibodies are capable to initiate the classical complement pathway.
Example data of C1q ELISA to determine binding of purified human complement component C1q to therapeutic antibodies: |
| | | | | | 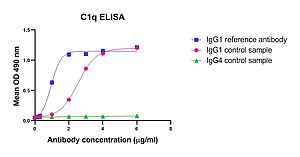 |
| | |
Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
ADCC of Rituximab |
| | | We perform antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) assays with freshly isolated PBMCs or magnetic bead separated lymphocyte subsets as effector cells. Specific target-cell death is quantified by flow cytometry or colorimetric determination of LDH release in the supernatant.
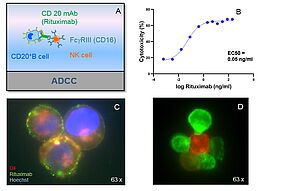
Example data
A: ADCC principle.
B: ADCC of Rituximab. Effector cells: PBMCs, Target cells: EBV-B-cells, E:T ratio 4:1.
C: Phenotypic analysis of target cells. EBV-B-cells (CD20+), Fluorescein labelled
Rituximab (green), Hoechst (blue), DiL (red).
D: ADCC: NK cells (green) interacting with target cells (EBV-B-cells, red). |
|
| |
|
| | | | |  |
|
| |
| | | | | | Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
CDC of IgG1 |
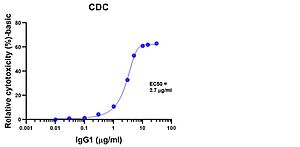
| | | We perform cell-based functional assays to detect CDC induced by baby rabbit complement. Target cell-death is measured by quantitation of cell metabolism (colorimetric readout).
Example data of CDC induced by IgG1: |
| | | | | |  |
|
| |
|
| |
| | | | | | | | | To receive more detailed information on our featured assays, contact us! |
|
|
|