Fc-mediated immunologic effector functions
Therapeutic antibodies and Antibody-Drug-Conjugates may elicit immunologic effector functions like Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC), Antibody Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP) and Complement Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC).
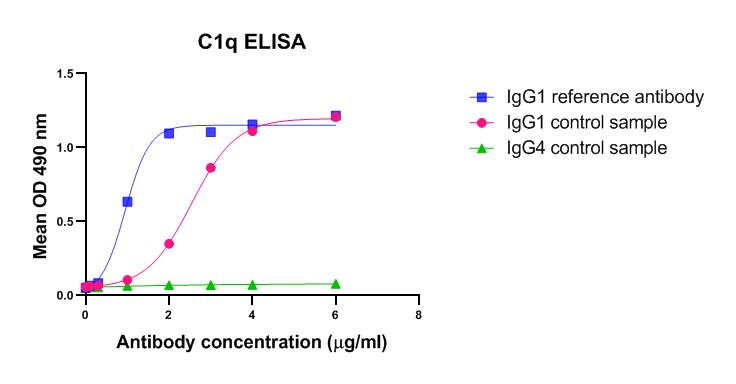
A critical step for induction of cell-mediated effector function is the binding of IgG antibodies to membrane antigens, followed by binding of the antibody’s Fc-part to Fcγ receptors. The complement Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC) is triggered by binding of antibody – antigen complexes to the complement component C1q.
Fcγ receptors
Fcγ RIIIa (CD16a) is considered to be the main contributor to ADCC. It is expressed on NK cells, monocytes/macrophages, T-cells, granulocytes and eosinophils. Due to genetic polymorphism Fcγ RIIIa, a conventional type I transmembrane protein, is expressed in two isoforms, a high binding and a low binding variant. Fcγ RIIIb (CD16b) is a GPI anchored protein, which lacks a transmembrane domain and is expressed on neutrophils. Despite its function is not yet fully understood, there are evidences that Fcγ RIIIb (CD16b) synergizes with Fcγ RIIa (CD32a), which is predominantly expressed on cells of the myeloid lineage and has been demonstrated to contribute to ADCC and ADCP. Fcγ RIIb/c is expressed on NK cells, monocytes/macrophages, B cells, neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. It acts as an inhibitor of cell activation and ADCP. Fcγ RI (CD64) is the only high affinity Fc Receptor. It is expressed on dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages, activated granulocytes and is involved in MHC dependent antigen presentation and cell activation.
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) is broadly expressed in different tissues. It prevents proteolytic degradation of IgGs thereby prolonging their half-life in circulation.
To characterize your product with respect to Fcγ receptor binding, cellular and cell-mediated effector functions IBR Inc. provides:
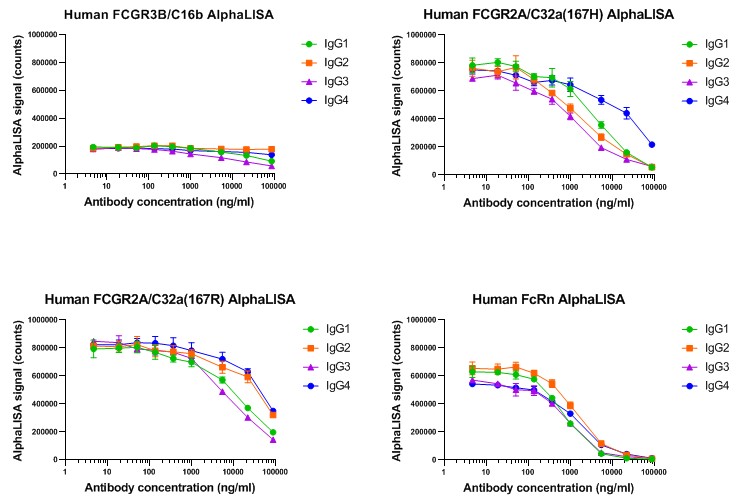
For non cell-based detection of human IgG binding to Fcγ receptors several ready-to-use AlphaLISA kits are available which cover the whole Fc receptor panel and in addition FcRn:
- FcγRIIIa - CD16a high and low binding variant
- FcγRIIIb - CD16b
- FcγRIIa - CD32a high and low binding variant
- FcγRIIb - CD32b
- FcγRI - CD64
- FcRn
Furthermore, IBR Inc. has capability to employ several other immunoassay technology platforms (ELISA, MSD ECL, Gyrolab, TR-FRET).
The binding affinity (Kd) of human IgGs to Fcγ receptors can be addressed using the Gyrolab™ Affinity solution. This provides an automated nanoliter-scale method and uses dedicated Gyrolab™ Affinity software that facilitates the design and evaluation of in-solution affinity experiments.
Our readers are suitable for measuring human IgG binding to Fcγ receptors on the cell surface using a Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) platform (Cisbio cellular binding platform). This platform provides TR-FRET reagents for competitive binding assays that cover the whole Fcγ receptor panel (FcγRIIIa - CD16a high and low binding variants; FcγRIIIb - CD16b; FcγRIIa - CD32a high and low binding variants; FcγRIIb - CD32b; FcγRI - CD64).
Alternatively, any commercially available cell line or gene reporter cell line expressing Fcγ receptors can be used to assess binding of antibodies by flow cytometry or gene reporter assays, respectively.
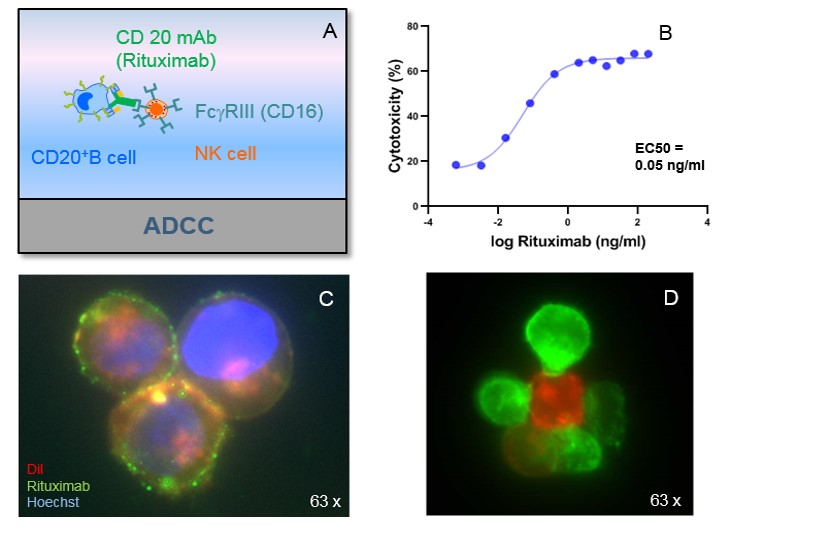
A: ADCC principle.
B: ADCC of Rituximab. Effector cells: PBMCs, Target cells: EBV-B-cells, E:T ratio 4:1.
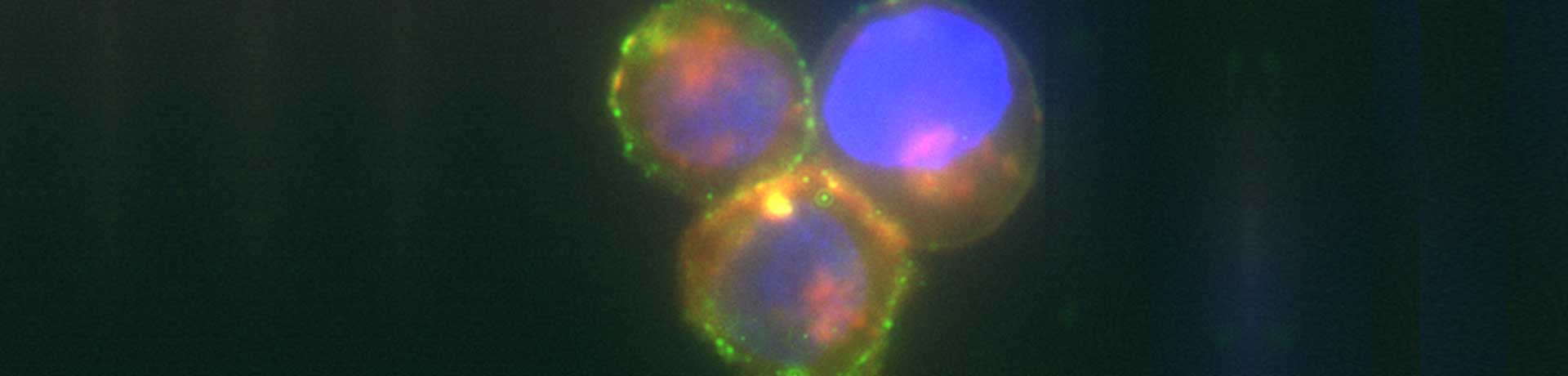
C: Phenotypic analysis of target cells. EBV-B-cells (CD20+), Fluorescein labelled
Rituximab (green), Hoechst (blue), DiL (red).
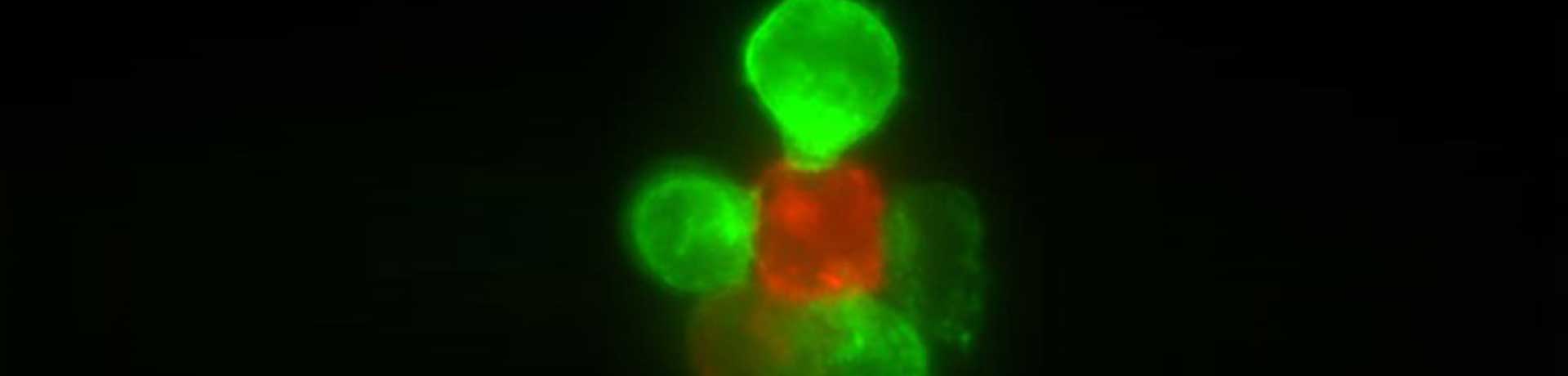
D: ADCC: NK cells (green) interacting with target cells (EBV-B-cells, red).
We perform antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) assays with PBMCs, magnetic bead separated NK cells or cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL’s) as effector cells. Specific target-cell death quantification by flow cytometry or colorimetric determination of LDH release in the supernatant.
IBR Inc. has capability to assess ADCP starting with monocytes (isolated from human PBMCs by magnetic cell isolation by Miltenyi Biotec). Monocytes are stimulated to differentiate into Monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) and polarized to generate either M1 or M2c macrophages. Macrophages are characterized by cytokine release and expression of surface markers. ADCP is determined by gating phagocytosed target-cells excluding target-cells only attached to the surface of the macrophages.
C1q assays
Binding of antibody – antigen complexes to the complement component C1q triggers the classical pathway of complement activation and results in the formation of the membrane attack complex leading to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Antibodies of the IgG subclasses IgG1, IgG2 and IgG3 (except IgG4) as well as IgM antibodies are capable to initiate the classical complement pathway.
To characterize your product with respect to complement activation IBR Inc. offers:
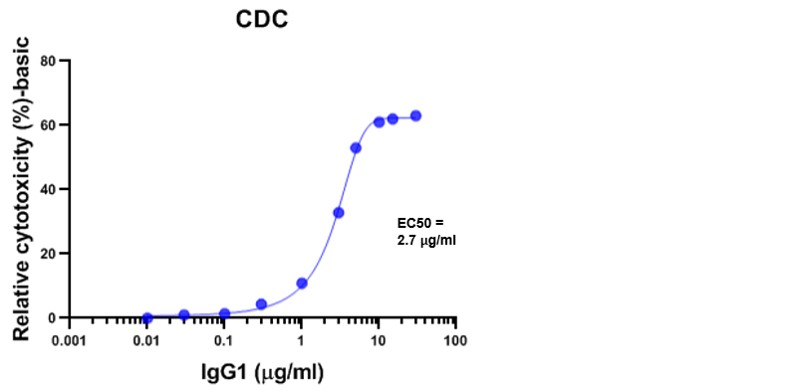
We perform cell-based functional assays to detect CDC induced by baby rabbit complement. Target cell-death is measured by quantitation of cell metabolism (colorimetric readout).
Submit a Question or Request
Simply fill out the form below and a member of our team will follow up with you shortly.